Situation about Automotive Chip Shortages
The auto industry has been short on semiconductor chips for two years, now the situation seems to be improving. But actually, some kinds of shortage still exist now.
But as vaccines became available and pandemic restrictions was removed,production restarted and things are getting better.
The problem began during the pandemic when a lot of chip supply was away from the auto industry and diverted to the consumer electronics industry in high demand. It is also associated with shutdowns around the world.
The analysts at AutoForecast Solutions expect that the chip shortage will result in around 3 million fewer vehicles being built in 2023; In 2022, automakers faced a production shortfall of 4.5 million vehicles due to shortages, down from 10.5 million lost vehicles in 2021.
Some people think that the shortage of automotive chips in the past is the kind of chips used for driver assistance functions, but in fact, it is not. The shortage is chips used to regular functions that everyone is more accustomed to.
Generally speaking, a traditional fuel vehicle may uses 200-300 semiconductor chips, while a modern car or new energy vehicle demand for chips over 1000. There are many types of these chips, to divide them into 5 groups according to their functions:Microcontrollers, intelligent Power Module, memory chips, communication chips and sensor. They are mainly used in the power system area, body area, remote control area, cockpit area, chassis area, and ADAS area.
Most future automotive-wafer demand will involve nodes of 90 nm and above because many vehicle controllers and electric powertrains, including electric drive inverters and actuators, rely on these mature chips, McKinsey reported.
The disadvantages of using more advanced chips in vehicles often outweigh the technological benefits, McKinsey explained. Since drive inverters and actuators require high voltages and currents, chips used in these applications don’t benefit from the high transistor density characteristic of smaller node sizes.
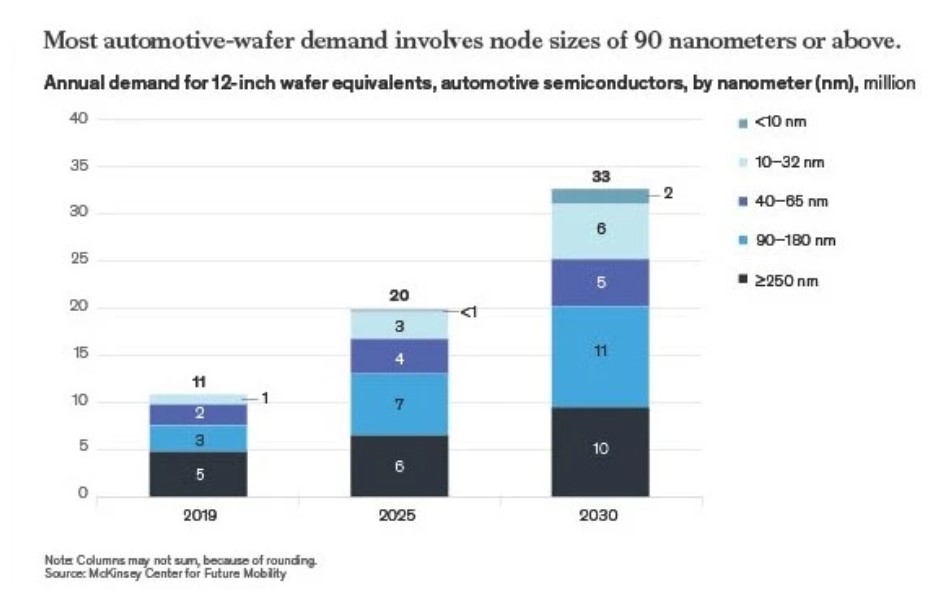
Source of data: McKinsey
Semiconductor companies are increasing production of 90 nm chips, “but our analysis suggests that the CAGR will remain at only 5 percent or so from 2021 through 2026—not enough to eliminate the supply – demand mismatch,” the firm added.
OEMs that rely on 90 nm chips for many applications have little incentive to migrate to smaller nodes because redesign incurs development and qualification costs, as well as more R&D staff, McKinsey explained.
Even if some automotive chip suppliers have recently started plans to build new fabs, it will take time to release their production capacity.
Generally speaking, the construction period of a fab takes about 1-2 years or even longer.
Infineon,the biggest automotive chip provider ,announced a 5-billion-euro ($5.35 billion) plant for power semiconductors in the German city of Dresden, which received the green light to begin construction last month. The plant is expected to be completed and start to output in 2026,in order to expand their position as a global supplier in the field of power systems.
In February 2023, TI announced it will build a second 300-mm wafer fab in Lehi, Utah, LFAB2. Construction is also expected to start in 2023 with production as early as 2026.
That’s why we believed that the auto chip shortage is improving but still remains for several years.
- No More
-
Next
Analog IC Market Insights In Q1 2023
